作者簡介:
胡竹林

現任:
北美智權教育訓練處
資深研究員
| 經歷: |
| ‧ |
高通顯示器 |
| |
微機電顯示器資深經理 |
| ‧ |
華晶科技 |
| |
工程部經理 |
| ‧ |
友達光電 |
| |
資深工程師 |
| ‧ |
加州大學洛杉磯分校 |
| |
電機研究所碩士 |
|
承接上一期的內容,再為讀者們介紹高錕博士的另一項發明專利,即是1977年獲證的”Multiple access fiber optical bus communication system(光纖多重讀取之光學匯流排通信系統)”,專利號碼為US4,017,149。
依專利說明書顯示,本發明提供了一種具有優越特性的多址讀取光纖傳輸系統,其中的任一光纖可在一個閉路系統中作為傳輸線之用。同時,系統設置多個光傳輸混頻器(mixer),每個混頻器可獨立連結多條傳輸線。另有不同可靠性程度的終端機(terminal),該終端機具有多個輸入和輸出埠,可藉由傳輸線與混頻器相連接。
圖一、光纖多重讀取之光學匯流排通信系統
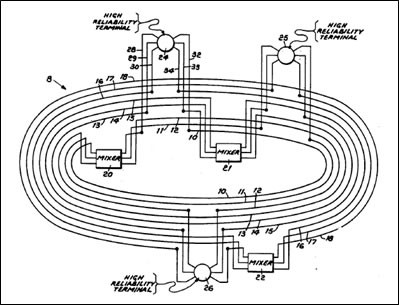
資料來源:USPTO, 4017149號專利
如圖一所示,該高可靠性之閉路匯流傳輸系統8包含10~18等9條傳輸光纖,依序分成3組線路,分別與混頻器20~22以及終端機24~26連接。其目的是確保當某一混頻器故障時,各終端機之間的輸出入信號仍可通行無阻。
同樣地,本發明的請求範圍僅有一個獨立項,外加17個附屬項,如下所示。
What is claimed is:
- A low loss fiber optical bus communication system comprising:
a plurality of optical transmission lines, each of which is formed into a closed loop;
a finite number of transmission line optical mixers operatively interconnected to a discrete number of said optical transmission lines, each of said mixers being independent of each other and forming a finite number of independent mixer transmission line loops; and
one or more optical access terminals connected to said transmission lines by being interconnected to at least one transmission line associated with at least one of said mixers said optical access terminals exceeding said finite number of transmission line optical mixers.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 1, wherein each of said transmission lines is a single optical fiber.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 1, wherein each of said mixers has the same number of transmission lines associated therewith forming a finite number of independent transmission loops having the identical number of input and output lines associated with each of said loops.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 1 wherein at least one of said terminals is a high reliability terminal having interconnections with at least one of said transmission lines associated with each of said mixers.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 1, wherein a plurality of terminals of varying reliability are interconnected to said independent loops, each of said terminals' reliability being determined by the number of its interconnections with the independent transmission line loops.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 5 wherein at least one terminal is a high reliability terminal which has at least one interconnection to one of said transmission lines in each of said independent loops.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 5 wherein at least one terminal is a low reliability terminal which has one input and one output interconnected to only one transmission line in one of said independent loops.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 1 wherein each terminal is connected to a transmission line by cutting one transmission line, the cut ends of said line constituting, respectively, the input and output lines to said terminal.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 8 wherein all of input lines' ends are driven by the same light source.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 8 wherein each of the input lines' ends is driven by a separate light source.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 8 wherein each of the input lines' ends is driven by separate light sources in parallel.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 8 wherein all of the output lines' ends terminate in a single photodetector.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 8 wherein each of the output lines' ends terminates in separate photodetectors.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 8 wherein each of the output lines' ends terminates in separate photodetectors in parallel.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 1 further including means in said one or more terminals for selectively determining the spectral wavelength of the light signals processed thereby.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 1 further including means in said one or more terminals for electronically multiplexing the light signals processed thereby.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 1 further including means in said one or more terminals for selectively determining the spectral wavelength of the light signals processed thereby and for electronically multiplexing the light signals processed thereby.
- The fiber optical bus system of claim 1 further including interconnecting fiber optical means for said one or more terminals wherein each said terminal may be remotely located with respect to said loops' location.
|
再來,筆者要介紹高錕博士的又一個發明專利,是其於1978年獲證的”Method for using on line optic fiber loss monitor”(光纖損失在線偵測器的使用方法),專利號碼為US4,081,258。
依照該專利說明書之內容指出,本發明提供了一種具有檢測光纖信號衰減特性的功能裝置。參照下圖之實施例所示,抽取出的光纖10被定位在一副支架12和14之上,使其已製備之光纖端面15位於光檢測器16內部。開口端18的設計必須確保檢測器22所偵測到的光信號,僅是通過該光纖10的端面15部位所發送者。
圖二、光纖損失在線偵測器的使用方法
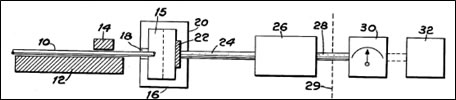
資料來源: USPTO, 4,081,258 號專利
如圖二所示,定義一熱輻射灰體光源信號經由光纖10發送,通過一過濾器20後,檢測器22可將接收到的光源信號轉換為電子信號,經由導線24傳遞給放大器26。該放大之信號經由導線28輸出到儀表指示器30以及圖形記錄器裝置32,以作為工程人員閱讀之用。
本案的特殊之處在於介紹發明背景時指稱,如何量測光纖的衰減特性,在本發明之前並無任何可供參考之先前技術,屬於創舉。
其四,筆者要介紹的發明專利是1980年獲證的”WATER RESISTANT HIGH STRENGTH FIBERS” (抗水氣侵蝕之高強度光纖),專利號碼為US4,183,621。
依照專利說明書之內容指出,本發明提供了一種可用以改善光纖因水氣侵蝕,引發機械疲勞而容易斷裂的製程方法。參照下圖之實施例所示,圖左是一個玻璃包覆在玻璃上的光纖10之橫截面,其中纖芯11是由摻雜的二氧化矽材料和由具有比纖芯11的折射率低的氧化矽材料製成纖壳12。石墨層13塗覆在玻璃光纖10的外表面,以便提供一個防水屏障。一種矽層14塗佈在碳層13之上,熱塑性護套15則包覆在矽層14之外。
圖三、抗水氣侵蝕之高強度光纖
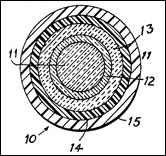 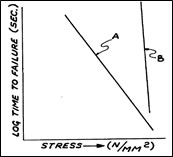 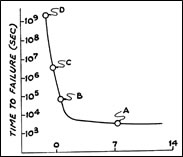
資料來源: USPTO, 4183621號專利
圖三中表示光纖的應力與失效時間之比較圖表,A為未塗覆抗水層之光纖,B為塗覆有抗水層之光纖。雖然在應力的延長測試下,光纖的故障原因尚未完全了解,可以確信的是它們都涉及當水氣接觸到外表面的二氧化矽微裂紋時,就會發生機械性破壞反應。
圖右表示光纖處在不同的酸鹼值環境下,其與失效時間之比較圖表,A表示測試環境的酸鹼值為7.0,B表示pH值為0的強酸環境,C表示一強酸、相對溼度50%、真空壓力為2x10-2 torr的測試環境,D表示塗覆有抗水層之光纖處於和C一樣的測試條件。
本專利技術在光纖材料的故障分析與製程方法的改良改善方面,堪稱做出劃時代的創舉。
本期筆者僅舉以上4篇高錕博士所研發之光纖技術專利供讀者們分享其研發創見。綜合光纖的技術內涵,我們可以清楚地了解到光纖的結構是包含一個纖芯(core),纖殼(cladding)以及外層的保護被覆(protective coating),纖芯與折射率(refractive index)較高的纖殼通常用高品質的矽石玻璃(silica glass)製成。其使用於工業應用上的優缺點,可歸納如下,
光纖通信技術的優點:
1.寬頻通信容量大、速率快,可做為影像、語音或文字資料高速通信之用。
2.光纜體積小,重量輕,可節省架設和運輸成本。
3.傳輸損耗小,中繼距離長,故傳輸性能穩定。
4.石英玻璃材質可耐水火,絕緣性佳且壽命長,不會產生短路、火花等危險事件。
5.具備雙向傳輸系統的可行性。
6.矽來源豐富,不虞匱乏且價格低廉。
7.不受電磁波干擾,資料竊取不易,保密性佳。
光纖通信技術的缺點:
光在光纖中傳遞會因散射、輻射、波吸收、耦合、連接、彎曲等因素,致使波幅漸減,歸納起來,光纖傳輸損失可分為兩大類:
(一)內在因素所引起的損失:
1.材料吸收損失可分成本質吸收及介入雜質損失
2.線性散射損失可分雷萊散射(Rayleigh scattering)及麥氏散射(Mie scattering)
3.非線性散射損失
4.洩漏模態(Leaky modes)
(二)光纖外在因素所引起的損失:
1.彎曲損失
2.微彎曲損失
3.輻射效應所致損失
4.接續損失為工程施工上最主要的考慮因素
5.製造,運送或佈放施工時受到的傷害
下一期專文中,筆者要為大家對於高錕博士所研發之光纖技術專利做進一步的分析,敬請期待。
更多歷期精采文章,請參閱智權報總覽 >>
|